| dc.contributor.author | El-Temsah, Yehia | |
| dc.contributor.author | Joner, Erik | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2017-12-21T14:47:28Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2017-12-21T14:47:28Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2013-06-03T11:32:47Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2013-06 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Chemosphere. 2013, 92 (1), 131-137. | nb_NO |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0045-6535 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/11250/2473602 | |
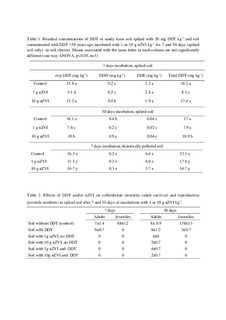
| dc.description.abstract | Nano-sized zero valent iron (nZVI) has been studied for in situ remediation of contaminated soil and ground water. However, little is known about its effects on organisms in soil and aquatic ecosystems. In this study, the effect of nZVI on degradation of DDT and its ecotoxicological effects on collembola (Folsomia candida) and ostracods (Heterocypris incongruens) were investigated. Two soils were used in suspension incubation experiments lasting for 7 and 30 d; a spiked (20 mg DDT kg−1) sandy soil and an aged (>50 years) DDT-polluted soil (24 mg DDT kg−1). These were incubated with 1 or 10 g nZVI kg−1, and residual toxicity in soil and the aqueous phase tested using ecotoxicological tests with collembola or ostracods. Generally, addition of either concentration of nZVI to soil led to about 50% degradation of DDT in spiked soil at the end of 7 and 30 d incubation, while the degradation of DDT was less in aged DDT-polluted soil (24%). Severe negative effects of nZVI were observed on both test organisms after 7 d incubation, but prolonged incubation led to oxidation of nZVI which reduced its toxic effects on the tested organisms. On the other hand, DDT had significant negative effects on collembolan reproduction and ostracod development. We conclude that 1 g nZVI kg−1 was efficient for significant DDT degradation in spiked soil, while a higher concentration was necessary for treating aged pollutants in soil. The adverse effects of nZVI on tested organisms seem temporary and reduced after oxidation. | nb_NO |
| dc.language.iso | eng | nb_NO |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier | nb_NO |
| dc.rights | Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internasjonal | * |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/deed.no | * |
| dc.title | Effects of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on DDT degradation in soil and its toxicity to collembola and ostracods | nb_NO |
| dc.type | Journal article | nb_NO |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | nb_NO |
| dc.description.version | acceptedVersion | nb_NO |
| dc.rights.holder | © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. | nb_NO |
| dc.source.pagenumber | 131-137 | nb_NO |
| dc.source.volume | 92 | nb_NO |
| dc.source.journal | Chemosphere | nb_NO |
| dc.source.issue | 1 | nb_NO |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.039 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 1032117 | |
| dc.relation.project | Norges forskningsråd: 186901 | nb_NO |
| cristin.ispublished | true | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.qualitycode | 1 | |